Background
Please refer PART 1 of this post for details on background and approach 1 to achieve cross account access for S3 bucket using Bucket polcies-
This post I will try to explain and demo how cross account access work with assume Role. This is way more secure and flexible that approach 1 (and generic too - approach 1 was specific to S3).This post assumes you have required setup and pre requisite knowledge mentioned in part 1. If you have not already I would highly recommend read PART1 first.
So we are going to try following. We already have IAM user in account A. And we will try accessing S3 bucket of Account B using assume cross account role.
NOTE : Remove bucket policy on the bucket if you have set any while following PART 1 of this post.
Changes to policy of IAM user of Account A
Since in this approach we are going to call assume role we need to give that access to the IAM user of Account A. So edit the inline policy of this IAM user to add following statement -
{
"Sid": "Stmt1511168304001",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
This will basically allow Account A IAM user to call assume role or any role of any other account.
Cross account role setup
Before we start with the code lets configure a cross account role in Account B.
Go to Account B IAM console of Account B and create a role as follows -
- Select a cross account role -
- Next provide Account ID of Account A in the input. Also select external ID requirement. External ID provided added security. (In abstract terms, the external ID allows the user that is assuming the role to assert the circumstances in which they are operating. It also provides a way for the account owner to permit the role to be assumed only under specific circumstances. The primary function of the external ID is to address and prevent the "confused deputy" problem - more details)
- Note the external ID we have used here. We are going to use it later . In this case we are using string called - SECRET
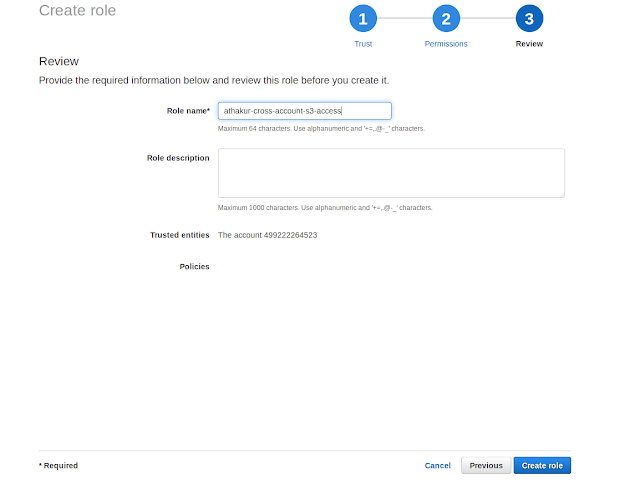
- Do not select any policies for now. We will come to that later. Just review , name your role and create it.
- Now once you have finished creating this role go to this role and select add inline policy and add below policy -
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1512121576471",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::aniket.help/*"
}
]
}
NOTE : If you need help creating policies you can go to - AWS policy generator and generate policy from there.
NOTE : The reason to do this is we did not want to give our cross account role entire s3 access or even access to other bucket than aniket.help bucket.
Finally note the the role arn. In this case it is -
- arn:aws:iam::706469024316:role/athakur-cross-account-s3-access
Assuming the role and cross account access
Now that our cross account role is setup lets go to the code where we can call assume role and access our S3 bucket.
Code is as follows -
public static boolean validateUpload() {
try {
BasicAWSCredentials credentials = new BasicAWSCredentials(awsAcessKeyId, awsSecretKey);
AssumeRoleRequest assumeRoleRequest = new AssumeRoleRequest().withRoleArn(ROLE_ARN)
.withExternalId(EXTERNAL_ID).withDurationSeconds(3600).withRoleSessionName("testSession");
AWSSecurityTokenService stsClient = AWSSecurityTokenServiceClientBuilder.standard()
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(credentials)).build();
AssumeRoleResult assumeResult = stsClient.assumeRole(assumeRoleRequest);
Credentials sessionCredentials = assumeResult.getCredentials();
BasicSessionCredentials basicSessionCredentials = new BasicSessionCredentials(
sessionCredentials.getAccessKeyId(), sessionCredentials.getSecretAccessKey(),
sessionCredentials.getSessionToken());
AmazonS3 s3client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(BUCKET_REGION)
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(basicSessionCredentials)).build();
s3client.putObject(BUCKET_NAME, "test.txt", "This is from cross account!");
} catch (AmazonServiceException ase) {
System.out.println(
"Caught an AmazonServiceException, which means your request made it to Amazon S3, but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message: " + ase.getMessage());
System.out.println("HTTP Status Code: " + ase.getStatusCode());
System.out.println("AWS Error Code: " + ase.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Error Type: " + ase.getErrorType());
System.out.println("Request ID: " + ase.getRequestId());
ase.printStackTrace();
return false;
} catch (AmazonClientException ace) {
System.out.println(
"Caught an AmazonClientException, which means the client encountered an internal error while trying to communicate with S3, such as not being able to access the network");
System.out.println("Error Message: {}" + ace.getMessage());
ace.printStackTrace();
return false;
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Got exception while validation bucket configuration.");
ex.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
Now run it in the same way we did in previous post (PART1). Output will be -
validated Upload : true
as expected.
NOTE : You can try different scenarios here like try changing the external id, or not using external ID at all, or playing around with policies. In all other cases you should get not authorized.
Similarly code for validateDownload() would be -
public static boolean validateDownload() {
try {
BasicAWSCredentials credentials = new BasicAWSCredentials(awsAcessKeyId, awsSecretKey);
AssumeRoleRequest assumeRoleRequest = new AssumeRoleRequest().withRoleArn(ROLE_ARN)
.withExternalId(EXTERNAL_ID).withDurationSeconds(3600).withRoleSessionName("testSession");
AWSSecurityTokenService stsClient = AWSSecurityTokenServiceClientBuilder.standard()
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(credentials)).build();
AssumeRoleResult assumeResult = stsClient.assumeRole(assumeRoleRequest);
Credentials sessionCredentials = assumeResult.getCredentials();
BasicSessionCredentials basicSessionCredentials = new BasicSessionCredentials(
sessionCredentials.getAccessKeyId(), sessionCredentials.getSecretAccessKey(),
sessionCredentials.getSessionToken());
AmazonS3 s3client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard().withRegion(BUCKET_REGION)
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(basicSessionCredentials)).build();
GetObjectRequest rangeObjectRequest = new GetObjectRequest(BUCKET_NAME, "test.txt");
rangeObjectRequest.setRange(0, 26);
S3Object s3Object = s3client.getObject(rangeObjectRequest);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s3Object.getObjectContent()));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String readLine;
while ((readLine = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(readLine);
}
System.out.println("Read File from S3 bucket. Content : " + sb.toString());
} catch (AmazonServiceException ase) {
System.out.println(
"Caught an AmazonServiceException, which means your request made it to Amazon S3, but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message: " + ase.getMessage());
System.out.println("HTTP Status Code: " + ase.getStatusCode());
System.out.println("AWS Error Code: " + ase.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Error Type: " + ase.getErrorType());
System.out.println("Request ID: " + ase.getRequestId());
ase.printStackTrace();
return false;
} catch (AmazonClientException ace) {
System.out.println(
"Caught an AmazonClientException, which means the client encountered an internal error while trying to communicate with S3, such as not being able to access the network");
System.out.println("Error Message: {}" + ace.getMessage());
ace.printStackTrace();
return false;
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Got exception while validation bucket configuration.");
ex.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
Read File from S3 bucket. Content : This is from cross account!
validated Download : true
Understanding the Workflow
Let's try to understand the workflow here
- We have credentials of IAM user of Account A.
- We use these credentials to make assume role call with the cross account role created in Account B to give Account A access
- We also use the external ID to validate Account A user is the authorized to make this call.
- When assumeRole call is made 1st thing that is checked is wherther this user has access to make this assume call. Since we had added this in the inline policy if IAM user of account A it goes through.
- Next check is whether assumeRole is successful. This checks if user calling this assumeRole is of same account configured in cross account role of Account B and that same external ID is used.
- Once these checks are cleared User from Account A will get temporary credentials corresponding to the role.
- Using these we can make call to S3 Upload/Download
- Now when these calls are made it is checked whether the role has access to GET/PUT of S3. if not access is denied. Since we explicitly added these policies for our cross account role this step is also accepted.
- And finally we have access to S3 GET/PUT.
- But note due to our role policy anyone assuming this role will have access to GET/PUT of aniket.help bucket only. No other AWS service or no other bucket of S3. This is why roles and policies are so important.
- Same goes with IAM user policy of user in Account A. It can only do sts assumerole call and has access to S3. Nothing else.
NOTE : Good thing about this approach is Account B can give access to KMS as well to the role and you can have a KMS based encryption as well (Which was not possible with previous approach).
To summarize this is diagram it can be as follows -
Again this is just a simplistic overview. All the things that happen in background are listed in workflow section above.